At least once, any of us here has asked a question on ChatGPT or Gemini, whether it’s about writing an email, solving a math problem, or simply what to prepare for a family dinner. From writing text to image generation or coding, the capabilities of AI assistants are undeniable.
But here’s a secret: the true power of AI isn’t just in what it can do but in how you ask it to do it. Many users find themselves frustrated when the quick answers they receive aren’t quite what they hoped for. Sometimes, the responses are too vague, too technical, or miss the mark. This isn’t always the AI’s fault – often, it comes down to how the question was asked. Just as with people, the way you phrase your question can make all the difference in the quality of the answer you get.
If your business seeks practical ways to frame queries, you’re landing at the right place. This article provides a strategic approach to communicating with AI to resolve complex problems, helping professionals receive detailed and valuable responses, reduce inefficiencies, and extract deeper insights from leading AI platforms.
Understanding How AI Works
Modern AI models are built on large-scale natural language processing and machine learning frameworks. These systems analyze massive volumes of data to generate human-like responses. The quality of those responses, however, depends heavily on how questions are formulated.
Recently, many AI chat assistants, including chat-based interfaces and Chrome extension tools, have been designed to offer users a seamless experience. Some allow access for free asks or ad-free experiences, while enterprise-grade solutions emphasize end-to-end encryption, compliance, and advanced configuration.
For enterprises evaluating AI chatbot technologies or broader AI tools, working with trusted providers is essential to ensure both accuracy and data security.
How to Craft Effective Questions
1. Be Clear and Specific
Ambiguous questions typically yield general or inaccurate outputs. Those queries make it hard for ChatGPT, Gemini, or any other AI tools and personal assistants to understand what you really want to generate an expected answer. To improve results, users should articulate questions with precision.
Example: Instead of typing “How do I improve customer service?”, use: “What are five AI-driven strategies to make customer service more efficient in a telecom enterprise?” Let’s try it and see the differences.
2. Add Relevant Context
You need to add context, such as business objectives, industry, or audience, so the AI can tailor its response. Contextual queries result in more personalized responses and greater relevance. The more clearly you explain, the deeper AI assistants understand your needs.
Example: Try to say, “I am leading digital transformation for a mid-size logistics firm. What AI solutions could reduce manual data entry in our invoicing process?” rather than just “AI solutions for manual data entry.”
3. Use Open-Ended Questions for Exploration
For strategic thinking, open-ended questions prompt the AI to analyze or explore topics instead of offering basic facts. They encourage the AI to gather information, identify patterns, make connections, and even generate novel ideas or solutions, mirroring a more human-like cognitive process. This approach is crucial for tasks requiring problem-solving, planning, and creative development, moving beyond simple information retrieval to true analytical engagement.
Example: Ask AI about “What AI trends are impacting enterprise cybersecurity strategies in 2025?” This question invites exploration of multiple factors, such as new technologies, threats, and strategic adaptations, rather than just listing facts.
4. Iterative Prompting and Response-Based Refinement
AI platforms are not one-off answer engines; they are response-based systems designed for multi-step collaboration. By refining questions based on the system’s prior output, users can guide the AI toward progressively better, more relevant results.
To achieve that, you can treat the interaction as a dialogue, not a transaction. Use phrases like “expand this idea,” “refine for a technical audience,” or “rewrite for clarity” in case you want to have deeper information in the output. Remember to break down requests into smaller components for better control over tone, depth, or structure.
Enterprise Use Case: A product marketing manager can draft a technical blog post with AI, then iteratively refine each section for executive readability, SEO alignment, and product accuracy.
5. Embedding Domain-Specific Context
Generic prompts result in generic answers. Embedding domain-specific contexts, such as industry, region, user type, or business goals, can dramatically improve the quality and applicability of responses.
Examples of Embedded Context: “As a healthcare compliance officer, explain how HIPAA affects AI-based patient data systems.” Or “Generate three options for a logistics company’s customer support script that must comply with EU consumer regulations.”
This strategy enables the AI to act less like a general knowledge tool and more like a specialized assistant attuned to your business’s needs.
6. Structured Prompt Engineering
This prompt engineering technique is all about structuring your instructions to help the AI get instant answers you want. It guides the AI’s response in terms of its layout and how it “sounds.”
- Role-based framing (“Act as a senior financial analyst”)
- Output format instructions (“List bullet points with explanations under each”)
- Priority directives (“Focus on security, scalability, and compliance”)
Structured prompt engineering approach works exceptionally well for simple tasks such as content creation, drafting policies, generating code, and improving how you communicate with stakeholders.
7. Leveraging Follow-Up Questions to Drive Precision
A well-phrased follow-up question is like a skilled interrogator, able to transform a generic AI response into something truly valuable and applicable to real-world scenarios. Instead of accepting a surface-level answer, a precise follow-up can push the AI to clarify information, challenge its assumptions, or expand on specific aspects of the initial output.
Think of it this way: If an AI tells you “AI will impact healthcare,” that’s a generic statement. But if you follow up with, “How might AI specifically improve diagnostic accuracy for rare diseases in rural clinics?” you’re guiding the AI to delve into a much more helpful and actionable area. This type of interaction allows you to pinpoint the exact information you need, moving from theoretical concepts to practical applications. It’s about turning a broad stroke into a finely detailed drawing, making the AI a more effective and insightful tool.
Strategic Examples: Here are some everyday questions your employees can use to drive precision in AI:
- “Can you cite supporting data for that recommendation?”
- “What are the risks of this solution in a high-regulation environment?”
- “Summarize this for a board-level presentation.”
Incorporating follow-up questions not only sharpens responses but also mimics executive-level inquiry and critical thinking workflows.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Interacting with AI
Even with advanced AI tools and large language models, the quality of output still depends heavily on the quality of the input. Professionals aiming to extract accurate answers, insights, or recommendations must avoid a few recurring mistakes when formulating queries.
Here are the most common pitfalls—and why they undermine the effectiveness of AI-generated responses:
1. Asking Overly Broad or Generic Questions
General prompts lack direction, forcing the AI to guess our intent or return high-level summaries with limited value.“Tell me about customer success.”
This question could yield a surface-level definition, a list of responsibilities, or broad strategies—none of which may match your actual need.
The best practice should be to narrow the scope and specify your intent. You’d better say:
“What are three KPIs enterprise SaaS companies use to measure customer success performance in the first 90 days after onboarding?”
2. Combining Unrelated Topics in a Single Query
Multi-topic prompts confuse the AI and dilute the response. Attempting to address disparate issues in one prompt often leads to fragmented answers or an incomplete response.
If you ask to “summarize this financial report and write an email to our vendor about changing the payment process”, the system may prioritize one part of the request or merge both in an unstructured way.
The best way is to break multi-part tasks into separate prompts for better accuracy and control.
- Step 1: Summarize the key metrics from this financial report, focusing on YoY growth and expense trends.
- Step 2: Draft an email to our vendor notifying them of a change in our payment schedule, referencing recent financial planning priorities.
3. Failing to Specify Goals, Users, or Business Constraints
AI performs best when it understands your request’s context, audience, and constraints. Skipping these details can result in content that is too technical, casual, or misaligned with business objectives.
When you want to “write a policy about remote work”, AI assistants could generate a generic template unsuitable for your industry, size, or legal jurisdiction. Instead, it’s recommended to include relevant business context. “Write a remote work policy for a 200-person fintech company operating in the U.S. and UK, with a hybrid team structure and security compliance requirements.”
Hence, you can ensure the AI generates tailored content aligned with your internal standards and external regulations.
4. Relying Solely on Initial Outputs Without Using Follow-Up Questions
AI models are designed for iterative improvement. Treating the first result as final often leaves valuable refinements unexplored.
For instance, the AI produces a draft presentation outline. Then, you must review and improve it with additional instructions, not just copy it as-is. Consequently, you miss an opportunity to align the tone, add examples, or tailor it to audience expectations.
To gain more qualified results, use follow-up questions to refine, challenge, or customize the initial response.
- “Rephrase this for a senior executive audience.”
- “Add an example relevant to the automotive industry.”
- “Include potential risks and mitigation strategies.”
Putting It All Together: A Real-World Example
To better understand how to craft effective questions using the principles above, consider the following enterprise scenario.
The context is that you are a product manager at a SaaS company preparing for a new product launch. You want to use an AI tool to generate initial marketing content, but the messaging must align with your brand tone, target mid-market B2B clients, and highlight integration with Microsoft Teams.
Poor Prompt Example:
Your input is “Write a product announcement email.” This lacks context, specificity, and any cues about the audience or product value. The output will likely be a generic and unusable draft.
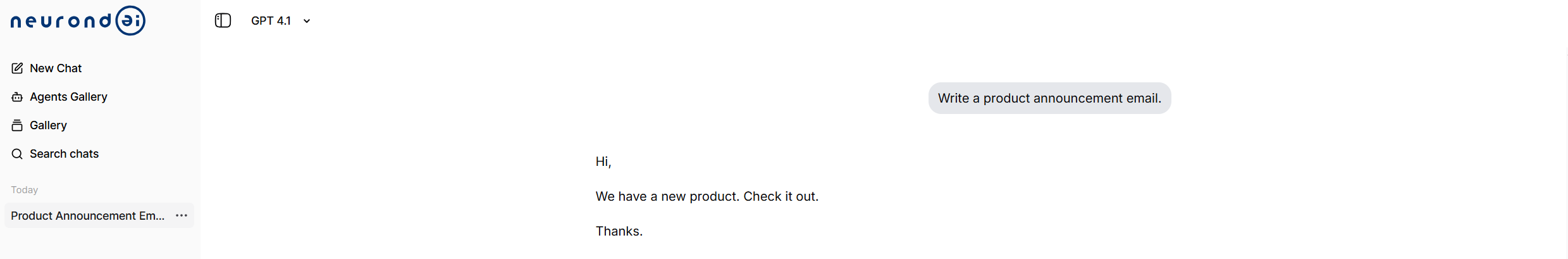
Improved Prompt Using Strategic Crafting:
We suggest using the following: “As a product marketing manager at a B2B SaaS company, write a professional announcement email for the launch of our new productivity tool that integrates with Microsoft Teams. The audience is IT directors and team leads at mid-market companies. Focus on time-saving features, ease of deployment, and compatibility with existing Microsoft 365 environments. Use a confident, informative tone suitable for enterprise buyers.”

Why this works:
- Clarity: The user clearly states what kind of content is needed.
- Context: The request includes company type, audience profile, and product positioning.
- Structure: The tone and focus are defined, guiding the AI toward relevant and accurate answers.
Here’s why this approach works so well: It brings clarity by explicitly stating the desired content type, provides essential context through details like the company type, audience, and product positioning, and establishes a clear structure by defining the tone and focus. Together, these elements effectively guide the AI to generate highly relevant and insightful responses.
Leading AI Assistant for Enterprise
| Platform |
Key Features |
Best For |
| ChatGPT |
Multi-purpose assistant, iterative conversation model |
Broad enterprise usage |
| Claude |
Privacy-focused, tailored for business users |
Legal, compliance, and confidential tasks |
| Perplexity |
Integrated with real-time search for verified insights |
Research-intensive teams |
| Gemini |
Connected to Google Workspace |
Productivity and document-based workflows |
| Poe |
Unified interface for multiple AI models |
Testing and comparison |
| Neurond Assistant |
Custom enterprise-grade AI assistant with security and scalability |
Mid- to large-sized businesses with tailored needs |
Selecting the right tool depends on your team’s technical requirements, compliance constraints, and expected use cases. The best AI Assistant will balance ease of use, data privacy, and response accuracy.
Why Effective AI Questioning is a Business Advantage
Knowing how to ask AI questions effectively is no longer a soft skill; it’s a strategic advantage and a game-changer. Informed inquiries, paired with the right AI tools, allow professionals to solve challenges faster, develop better ideas, and support decisions with accurate information.
Don’t be afraid to experiment with different inputs to determine what works for you. So remember, if you’re having trouble asking AI questions, try the above practices. Once you refine how your team interacts with AI chatbots and online tools, you unlock the true potential of artificial intelligence as a scalable, insightful, and secure partner in your enterprise’s growth.
If you’re evaluating how AI can support your workflows, Neurond offers enterprise-grade assistants tailored to your business challenges. Contact us to explore a solution that meets your goals.









